Abstract
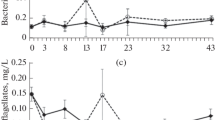
The purpose of this study was to determine how zebra mussels affected cladoceran community structure under eutrophic conditions. We conducted a mesocosm study where we manipulated the presence of zebra mussels and the presence of large-bodied Daphnia (Daphnia magna and Daphnia pulicaria). We also conducted a complimentary life-table experiment to determine how water from the zebra mussel treatment affected the life history characteristics of the cladoceran species. We anticipated that small- and large-bodied cladoceran species would respond differently to changes in algal quality and quantity under the effects of zebra mussels. Large-bodied Daphnia successfully established in the zebra mussel treatment but failed to grow in the control. We did not observe positive relationships between food concentrations and cladoceran abundances. However, the phosphorus content in the seston indicated that food quality was below the threshold level for large-bodied cladocerans at the beginning of the experiment. We believe that zebra mussels quickly enhanced the phosphorus content in the seston due to the excretion of inorganic phosphorus, thus facilitating the development of large-bodied Daphnia. In conclusion, our results suggest that zebra mussels can alter the phosphorus content of seston in lakes and this can affect the dynamics of crustacean zooplankton.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, T. & D. O. Hessen, 1991. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus content of freshwater zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 36: 807–814.
Baker, S. M., J. S. Levington, J. P. Kurdziel & S. E. Shumway, 1998. Selective feeding and biodeposition by zebra mussels and their relation to changes in phytoplankton composition and seston load. Journal of shellfish research 17: 1207–1213.
Baker, S. M., J. S. Levinton & J. E. Ward, 2000. Particle transport in the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas). The Biological Bulletin 199: 116–125.
Balushkina, E. V. & G. G. Vinberg, 1978. Relationship between body weight and size in plankton animals. In Vinberg, G. G. (ed.), Experimental and field investigations of biological production in lakes Zoological Institute. Academy of Sciences USSR, Leningrad: 58–72.
Bergström, A.-K., D. Karlsson, J. Karlsson & T. Vrede, 2015. N-limited consumer growth and low nutrient regeneration N: P ratios in lakes with low N deposition. Ecosphere. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES14-00333.1.
Brett, M., D. C. Müller-Navarra & S.-K. Park, 2000. Empirical analysis of the effect of phosphorus limitation on algal food quality for freshwater zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1564–1575.
Brooks, J. L. & S. I. Dodson, 1965. Predation, body size and composition of plankton. Science 150: 28–35.
Chesson, P., 2000. Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 31: 343–366.
Chróst, R. J., T. Adamczewski, K. Kalinowska & A. Skowrońska, 2009. Abundance and structure of microbial loop components (bacteria and protists) in lakes of different trophic status. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 19: 858–868.
DeMott, W. R., 1986. The role of taste in food selection by freshwater zooplankton. Oecologia 69: 334–340.
DeMott, W. R. & R. D. Gulati, 1999. Phosphorus limitation in Daphnia: evidence from a long term study of three hypereutrophic Dutch lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 44: 1557–1564.
Feniova, I., P. Dawidowicz, M. I. Gladyshev, I. Kostrzewska-Szlakowska, M. Rzepecki, V. Razlutskij, et al., 2015. Experimental effects of large-bodied Daphnia, fish and zebra mussels on cladoceran community and size structure. Journal of Plankton Research 37: 611–625.
Ghilarov, A. M., 1981. Coexistence of closely related species of Daphnia (Cladocera, Crustacea): one more display of plankton paradox. Doklady Akademii Nauk 257: 251–253.
Gladyshev, M. I., V. I. Kolmakov, O. P. Dubovskaya & E. A. Ivanova, 2000. Studying of algae food composition of Daphnia longispina during bluegreen bloom of eutrophic pond. Doklady Akademii Nauk 371: 556–558.
Gladyshev, M. I., N. N. Sushchik, A. A. Kolmakova, G. S. Kalachova, E. S. Kravchuk, O. N. Makhutova & E. A. Ivanova, 2007. Seasonal correlations of elemental and v-3 PUFA composition of seston and dominant phytoplankton species in a eutrophic Siberian Reservoir. Aquatic Ecology 41: 9–23.
Gladyshev, M., N. N. Sushchik, O. P. Dubovskaya, O. N. Makhutova & G. S. Kalachova, 2008. Growth rate of Daphnia feeding on seston in a Siberian reservoir: the role of essential fatty acid. Aquatic Ecology 42: 617–627.
Gladyshev, M. I., N. N. Sushchik, O. P. Dubovskaya, Z. F. Buseva, O. N. Makhutova, E. B. Fefilova, et al., 2015. Fatty acid composition of Cladocera and Copepoda from lakes of contrasting temperature. Freshwater Biology 60: 373–386.
Gliwicz, Z. M., 2003. Between hazards of starvation and risk of predation: the ecology of off-shore animals Excellence in Ecology, Book 12. International Ecology Institute, Oldendorf/Luhe.
Hartwich, M., D. Martin-Creuzburg, K.-O. Rothhaupt & A. Wacker, 2012. Oligotrophication of a large, deep lake alters food quantity and quality constraints at the primary producer-consumer interface. Oikos 121: 1702–1712.
Hessen, D. O. & T. Andersen, 2008. Excess carbon in aquatic organism and ecosystems: physiological, ecological and evolutionary implications. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 1685–1696.
Higgins, S. N. & M. J. Vander Zanden, 2010. What a difference a species makes: a meta-analysis of dreissenid mussel impacts on freshwater ecosystems. Ecological Monographs 80: 179–196.
Johnson, C. R. & C. Luecke, 2012. Copepod dominance contributes to phytoplankton nitrogen deficiency in lakes during periods of low precipitation. Journal of Plankton Research 34: 345–355.
Karatayev, A. Y., L. E. Burlakova & D. K. Padilla, 1997. The effects of Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas) invasion on aquatic communities in Eastern Europe. Journal of Shellfish Research 16: 187–203.
Karatayev, A. Y., L. E. Burlakova & D. K. Padilla, 2002. Impacts of Zebra Mussels on Aquatic Communities and Their Role as Ecosystem Engineers. In Leppakoski, E. S., S. Gollasch & S. Olenin (eds), Invasive Aquatic Species of Europe. Distribution, Impacts and Management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 433–446.
Kelly, D. W., L.-M. Herborg & H. J. MacIsaac, 2010. The Zebra Mussel in Europe. In van der Velde, G., S. Rajagopal & A. de Bij Vaate (eds), Ecosystem Changes Associated with Dreissena Invasions Recent Developments and Emerging Issues, 199–209. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden: 199–210.
Makhutova, O. N., M. I. Gladyshev, A. A. Sylaieva, N. N. Sushchik, G. S. Kalachova, A. A. Protasov & I. A. Morozovskaya, 2013. Feeding spectra of bivalve mollusks Unio and Dreissena from Kanevskoe Reservoir, Ukraine: are they food competitors or not? Zoological Studies 52: 56, http://www.zoologicalstudies.com/content/52/1/56.
McCauley, E., W. W. Murdoch & R. Nisbet, 1990. Growth, reproduction, and mortality of Daphnia pulex Leyding: life at low food. Functional Ecology 4: 505–514.
Müller-Navarra, D. C., 1995. Evidence that a highly unsaturated fatty acid limits Daphnia growth in nature. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 132: 297–307.
Müller-Navarra, D. & W. Lampert, 1996. Seasonal patterns of food limitation in Daphnia galeata: separating food quantity and food quality effects. Journal of Plankton Research 18: 1137–1157.
Müller-Navarra, D. C., M. T. Brett, A. M. Liston & C. R. Goldman, 2000. A highly unsaturated fatty acid predicts carbon transfer between primary producers and consumers. Nature 403: 74–77.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Petrosyan, V. G., 2014. The integrated database management system and the statistical analysis of biological data. Biosystem office. Russian Federal Service for Intellectual Property, Certificate 2014663194, Date of registration—18.12.2014 http://www1.fips.ru/fips_servl/fips_servlet?DB=EVMDocNumber = 2014663194TypeFile = html
Pijanowska, J., P. Dawidowicz, A. Howe & L. J. Weider, 2006. Predator-induced shifts in Daphnia life-histories under different food regimes. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 167: 37–54.
Porter, K. G., Y. S. Feig & E. F. Vetter, 1983. Morphology, flow regimes, and filtering rates of Daphnia, Ceriodaphnia, and Bosmina fed natural bacteria. Oecologia 58: 156–163.
R Core Team, 2017. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Raikow, D. F., O. Sarnelle, A. E. Wilson & S. K. Hamilton, 2004. Dominance of the noxious cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa in low-nutrient lakes is associated with exotic zebra mussels. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 482–487.
Ravet, J. L., J. Persson & M. T. Brett, 2012. Threshold dietary polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrations for Daphnia pulex growth and reproduction. Inland Waters 2: 199–209.
Romanovsky, Yu E & I Yu Feniova, 1985. Competition among Cladocera: effect of different levels of food supply. Oikos 44: 243–252.
Semenchenko, V. P., V. I. Razlutskij, I. Y. Feniova & D. N. Aibulatov, 2007. Biotic relations affecting species structure in zooplankton communities. Hydrobiologia 579: 219–231.
Shea, K. & P. Chesson, 2002. Community ecology as a framework for biological invasions. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 17: 170–176.
Sikora, A. & P. Dawidowicz, 2014. Do the presence of filamentous cyanobacteria and an elevated temperature favor small-bodied Daphnia in interspecific competitive interactions? Fundamental and Applied Limnology 185: 307–314.
Sikora, A. B., Th Petzoldt, P. Dawidowicz & E. von Elert, 2016. Demands of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in Daphnia: are they dependent on body size? Oecologia 182: 405–417.
Sinicyna, O. O. & B. Zdanowski, 2007. Development of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha (Pall.), population in a heated lakes ecosystem. II. Life strategy. Archives of Polish Fisheries 15: 387–400.
Sperfeld, E. & A. Wacker, 2011. Temperature- and cholesterol-induced changes in eicosapentaenoic acid limitation of Daphnia magna determined by a promising method to estimate growth saturation thresholds. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 1273–1284.
Standard Methods, 2005. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, USA.
Sterner, R. W., 1997. Modeling interactions of food quality and quantity in homeostatic consumers. Freshwater Biology 38: 473–481.
Sterner, R. W., 1998. Demography of a natural population of Daphnia retrocurva in a lake with low food quality. Journal of Plankton Research 20: 471–489.
Sterner, R. W. & J. J. Elser, 2002. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
Sterner, R. W. & D. O. Hessen, 1994. Algal nutrient limitation and the nutrition of aquatic herbivores. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 25: 1–29.
Sterner, R. W. & K. L. Schulz, 1998. Zooplankton nutrition: recent progress and a reality check. Aquatic Ecology 32: 261–279.
Taipale, S. J., K. Vuorio, M. T. Brett, E. Peltomaa, M. Hiltunen & P. Kankaala, 2016. Lake zooplankton δ13C values are strongly correlated with the δ13C values of distinct phytoplankton taxa. Ecosphere 7: e01392. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.1392.
Tilman, D., 2004. Niche tradeoffs, neutrality, and community structure: a stochastic theory of resource competition, invasion, and community assembly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101: 10854–10861.
Urabe, J., J. Clasen & R. W. Sterner, 1997. Phosphorus limitation of Daphnia growth: is it real? Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1436–1443.
Urabe, J. & R. W. Sterner, 1996. Regulation of herbivore growth by the balance of light and nutrients. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93: 8465–8469.
Vanderploeg, H. A., T. F. Nalepa, D. J. Jude, E. L. Mills, K. T. Holeck, J. R. Liebig, et al., 2002. Dispersal and emerging ecological impacts of Ponto-Caspian species in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 59: 1209–1228.
Vanni, M. J., 2002. Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 33: 341–370.
Wacker, A. & E. von Elert, 2001. Polyunsaturated fatty acids: evidence for non-substitutable biochemical resources in Daphnia galeata. Ecology 82: 2507–2520.
Wilson, A. E., 2003. Effects of zebra mussels on phytoplankton and ciliates: a field mesocosm experiment. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 905–915.
Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A. & P. Frankiewicz, 2011. The impact of pelagic (Daphnia longispina) and benthic (Dreissena polymorpha) filter feeders on chlorophyll and nutrient concentration. Limnologica 41: 191–200.
Acknowledgements
Experiments were performed with the support by the Polish National Science Centre (UMO-2016/21/B/NZ8/00434). Statistical analysis and data interpretation for publication were supported by Russian Science Foundation (Grant No:16-14-10323). The elemental and biochemical analyses were supported by Russian Federal Tasks of Fundamental Research (Project No. 51.1.1), by the Council on Grants from the President of the Russian Federation for support of Leading Scientific Schools (Grant NSh-9249.2016.5) and by Federal Tasks of Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation for Siberian Federal University (Project No. 6.1504.2017/PCh).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Karl E. Havens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feniova, I., Dawidowicz, P., Ejsmont-Karabin, J. et al. Effects of zebra mussels on cladoceran communities under eutrophic conditions. Hydrobiologia 822, 37–54 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3699-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3699-4